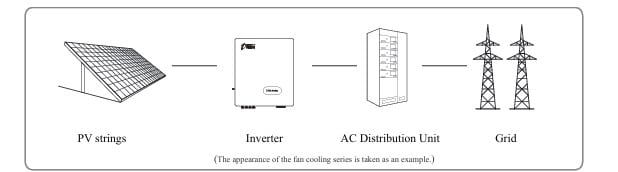
Unleash Solar Power with the Chint 50 KW On-Grid Inverter
If you’re looking to harness the sun’s energy like a pro, the Chint SCA50K-T-EU Three-Phase String Inverter is your ultimate partner. This 50 KW on-grid inverter is a game-changer for solar energy systems, combining cutting-edge technology with user-friendly features. Whether you’re a solar enthusiast or a professional installer, this inverter is designed to make your life easier while maximizing energy output. Let’s dive into what makes the Chint 50 KW on-grid inverter a standout choice.
Why Choose the Chint 50 KW On-Grid Inverter?
The Chint SCA50K-T-EU is more than just an inverter; it’s a smart energy solution. With a peak efficiency of 98.4%, it ensures that every ray of sunlight is converted into usable power. Its three Maximum Power Point Trackers (MPPTs) allow you to connect multiple PV modules with ease, even if they’re facing different directions or experiencing shading. Each MPPT supports a maximum input current of 30A, making it compatible with a wide range of solar panels.
You May Also Like: Unlocking Solar Power Potential with the Chint 125 KW On-Grid Inverter
Key Features That Set It Apart
- High Efficiency and Performance
The Chint 50 KW inverter boasts a 98.20% maximum efficiency, ensuring minimal energy loss during conversion. Its Euro efficiency of 98% means it performs consistently well under real-world conditions. - Flexible DC Input Options
With a maximum DC voltage of 1100V and an MPPT operating range of 160-1000V, this inverter adapts to various solar setups. It starts operating at just 180V, making it ideal for low-light conditions. - Robust AC Output
Delivering a rated AC power of 50kW and a maximum AC power of 55kVA, this inverter is perfect for commercial and industrial applications. Its power factor of >0.99 ensures smooth integration with the grid. - Advanced Protection Mechanisms
Safety is a top priority. The Chint SCA50K-T-EU comes with DC reverse connection protection, AC short-circuit protection, and leakage current protection. It also features surge protection and Arc Fault Circuit Interruption (AFCI) to prevent fire hazards. - Durable and Reliable Design
Built to withstand harsh environments, this inverter has an IP66 rating, making it dustproof and waterproof. It operates seamlessly in temperatures ranging from -25°C to +60°C and at altitudes up to 4000 meters. - Smart Monitoring and Communication
Stay in control with the LED display and Bluetooth-enabled app. The inverter supports RS485, Wi-Fi, and optional 4G communication, allowing you to monitor performance remotely.
Technical Specifications at a Glance
- DC Input: Max. DC Voltage: 1100Vdc, MPPT Operating Voltage Range: 160-1000Vdc, Start Voltage: 180Vdc
- AC Output: Rated AC Power: 50kW, Max. AC Power: 55kVA, Grid Frequency: 50/60Hz
- Efficiency: Max. Efficiency: 98.20%, Euro Efficiency: 98%
- Protection: DC reverse connection, AC short circuit, leakage current, surge protection, AFCI
- Environment: IP66 rating, Operating Temperature: -25°C to +60°C, Altitude: 4000m
- Communication: RS485, Wi-Fi, 4G (optional), LED display, Bluetooth app
You May Also Like: Best Budget Phones for Students: Affordable Picks
Who Is It For?
The Chint 50 KW on-grid inverter is ideal for commercial and industrial solar installations. Whether you’re powering a factory, a warehouse, or a large residential complex, this inverter delivers unmatched performance. Its transformerless design ensures lightweight construction and easy installation, while its high power output makes it suitable for large-scale projects.
Why You’ll Love It
- Cost-Effective: High efficiency means lower energy bills and faster ROI.
- User-Friendly: Easy to install, monitor, and maintain.
- Future-Proof: Compatible with a wide range of PV modules and grid requirements.
- Eco-Friendly: Helps reduce your carbon footprint by maximizing solar energy use.
Final Thoughts
The Chint SCA50K-T-EU Three-Phase String Inverter is a powerhouse of innovation, efficiency, and reliability. Whether you’re upgrading your solar system or starting from scratch, this 50 KW on-grid inverter is a smart investment. With its advanced features, robust design, and user-friendly interface, it’s no wonder the Chint 50 KW inverter is a favorite among solar professionals.
Ready to take your solar energy game to the next level? The Chint 50 KW on-grid inverter is here to make it happen. Say goodbye to energy waste and hello to a brighter, greener future!
You May Also Like: What Is Deep Work?
By choosing the Chint 50 KW On-Grid Inverter, you’re not just investing in a product; you’re investing in a sustainable future. So, why wait? Go solar with Chint and experience the power of innovation today!