Maximize Efficiency with SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter
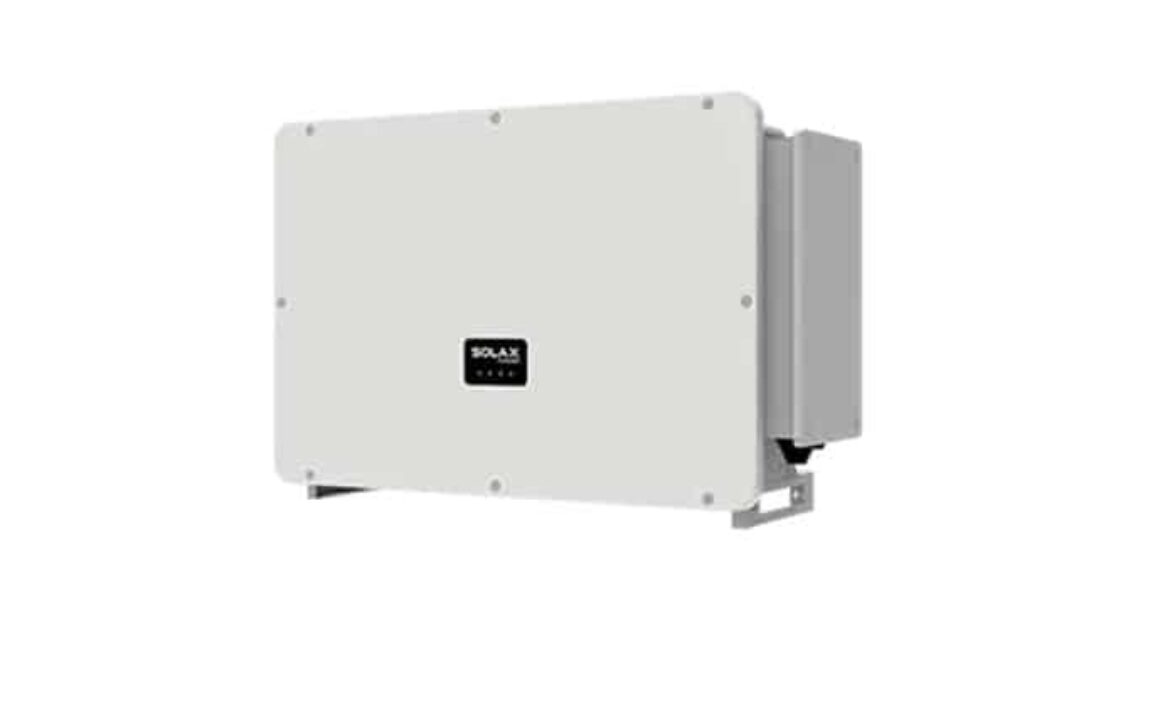
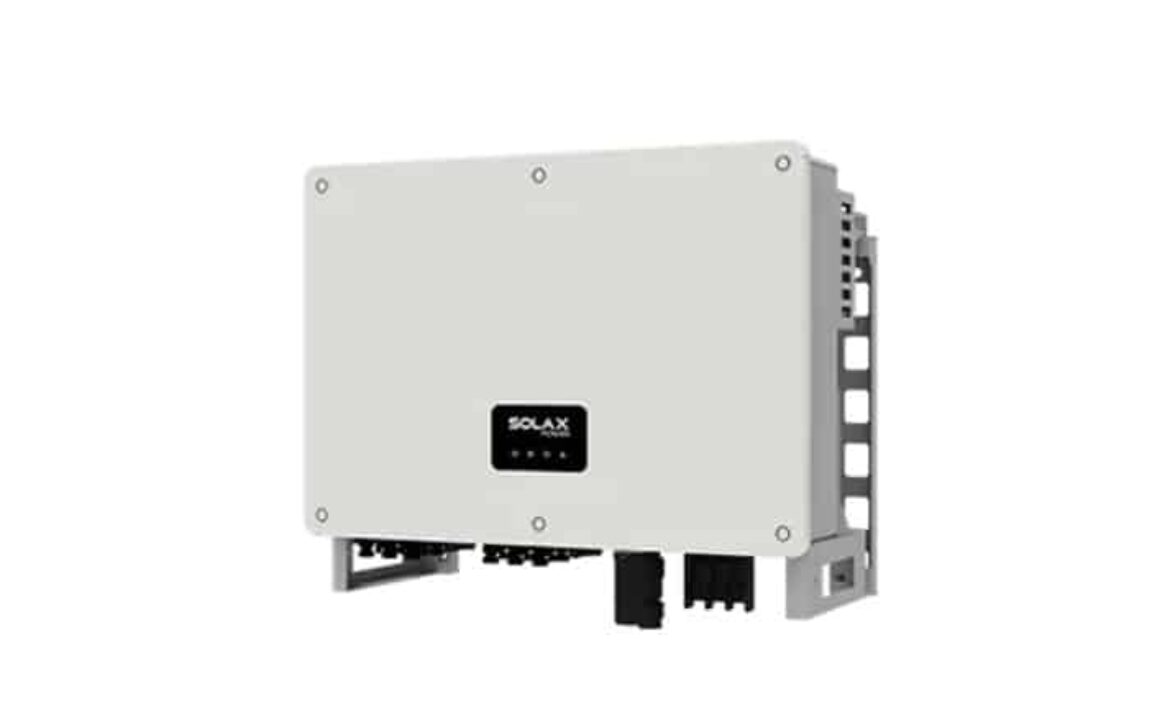
When harnessing solar power efficiently and reliably, the SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter (X3-MIC-10K-G2) stands out as a top-tier solution. This high-performance inverter combines cutting-edge technology with robust safety features, ensuring optimal power generation for residential and commercial solar installations. Let’s dive into the details of this inverter and uncover why it’s a game-changer in the solar energy market.
You May Also Like: Comprehensive Review of SolaX 110 KW Three Phase Inverter

Flexible Adaptability
The SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter is engineered with adaptability in mind, making it an excellent choice for diverse solar setups. Here’s how it excels in flexibility:
- Built-in Export Power Control: Manage power output effectively to align with grid regulations and maximize self-consumption.
- 200% DC Oversizing: The inverter supports double the rated DC input, allowing you to connect more solar panels for higher energy yields.
- 110% AC Overloading Output: Provides an extra edge by delivering more power during peak demands, enhancing performance in real-world conditions.
- Wide MPPT Range (120–980 V): This ultra-wide range ensures maximum power point tracking across varying weather conditions, increasing overall energy efficiency.
- Low Start-Up Voltage (150 V): Enables earlier power generation in low-light conditions, such as mornings or overcast days.
You May Also Like: SolaX 50 KW Three Phase Inverter: Efficiency & Innovation
Unparalleled Efficiency
Efficiency is at the core of the X3-MIC-10K-G2, designed to ensure that every watt of solar energy is put to good use:
- Maximum Efficiency of 98.3%: Industry-leading efficiency ensures minimal energy loss during DC-to-AC conversion.
- European Efficiency of 97.8%: Tested for real-world performance, this inverter guarantees reliable output even under variable loads.
- 32A per MPPT Tracker: High input current handling capacity supports larger and more powerful solar panels.
- Global MPP Scan: A built-in feature that continuously optimizes performance by scanning for the best power points.
Intelligent Design
Modern solar systems demand not only performance but also smart functionality, and the SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter delivers on all fronts:
- IP66 Protection: Dust-tight and waterproof, ensuring durability even in the harshest environmental conditions.
- Compact Dimensions: Measuring just 342 × 434 × 156 mm and weighing 17 kg, it’s easy to install in tight spaces.
- 24/7 Monitoring: Stay connected with multiple communication options, including Wi-Fi, LAN, and 4G, enabling real-time system performance tracking.
- Smart Load Management: Integrate with devices like heat pumps or smart EV chargers for intelligent energy usage.
- Ultra-High Power Density: Packs exceptional power into a compact unit, optimizing space without compromising performance.
You May Also Like: 10 Inspirational Books for Leaders to Ignite Your Leadership Journey
Assured Safety
Safety is a priority in any solar system, and the X3-MIC-10K-G2 comes equipped with advanced protection features:
- Type II SPD on Both AC & DC Sides: Optional surge protection devices safeguard your system against voltage spikes.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI): Available as an optional feature, it provides an additional layer of safety by preventing electrical fires caused by arc faults.
- Overload and Short Circuit Protections: Comprehensive protections ensure the longevity and reliability of your inverter.
- Active Anti-Islanding Technology: Maintains grid stability by detecting grid failures and automatically shutting down the inverter when necessary.
Why Choose the SolaX X3-MIC-10K-G2?
The SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter isn’t just a device—it’s a comprehensive energy management solution. Here’s why it’s an excellent choice for your solar power needs:
- Exceptional Performance: With its high efficiency, wide MPPT range, and support for oversized arrays, the inverter maximizes energy production in every scenario.
- Smart Connectivity: Stay in control with robust monitoring options and intelligent energy management features.
- Reliable and Durable: Built to withstand tough environmental conditions with IP66 protection and advanced safety protocols.
- Easy Installation: Compact and lightweight, it’s designed for hassle-free setup and integration into any solar system.
You May Also Like: The Best Gaming Tablets for 2024
Technical Specifications at a Glance
PV Input
- Max. recommended PV array power: 20 kWp
- Start-up voltage: 150 V
- MPPT voltage range: 120–980 V
AC Output
- Rated output power: 10,000 W
- Nominal AC voltage: 220/380 V or 230/400 V
Efficiency
- Maximum Efficiency: 98.3%
- European Efficiency: 97.8%
Environmental Limits
- Ingress protection: IP66
- Max. operating altitude: 4000 m
- Humidity: 0–100% (condensing)
Conclusion
The SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter (X3-MIC-10K-G2) is a testament to innovation and efficiency in the solar energy industry. Whether you’re optimizing a residential system or powering a commercial project, this inverter delivers unmatched reliability, safety, and performance. With its high-efficiency design, intelligent features, and robust safety protocols, it’s the perfect partner for a future powered by clean energy.
Experience the difference with the SolaX 10 KW Three-Phase Inverter—your gateway to smarter and more sustainable solar energy.